Hello World program step by step execution –
//Header file
#include <stdio.h>
//main function
int main()
{
// This is a simple "Hello, World!" program
printf("Hello, World!\n");
return 0;
}Now, let’s break down the program and go through its execution step by step:
See also – The history of C programming
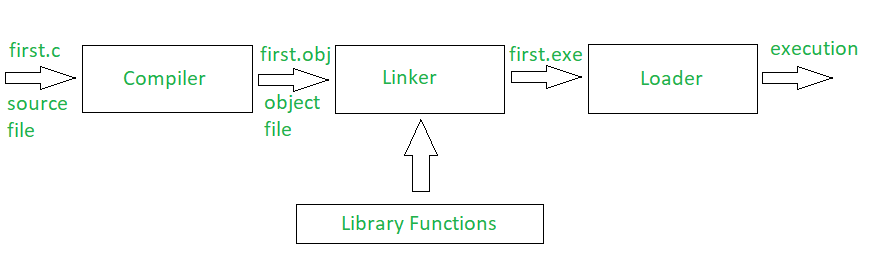
- Preprocessor Directives:
#include <stdio.h>- The #include directive is used to include the contents of the standard input/output library (stdio.h). This library provides functions like printf and scanf for input and output operations.
- Function Declaration:
int main() {- The program starts executing from the main function. It is the entry point of every C program.
- int is the return type of the main function, and main takes no parameters in this case.
- Opening Brace
{and Comments:
// This is a simple "Hello, World!" program- Comments are for human-readable explanations and do not affect the program’s execution. They start with
//for single-line comments.
- Print Statement:
printf("Hello, World!\n");- The printf function is used to print text to the console. In this case, it prints “Hello, World!” followed by a newline (\n) character to move the cursor to the next line.
- Closing Brace
}andreturnstatement:
return 0;
}- The return 0; statement indicates that the program executed without any errors. The value 0 is returned to the operating system, indicating successful execution.
Now, let’s summarize the execution steps:
- The preprocessor includes the contents of the stdio.h library.
- The program starts executing from the main function.
- The printf function prints “Hello, World!\n” to the console.
- The return 0; statement indicates successful execution, and the program exits.
When you compile and run this program, you should see the output:
Hello, World!Keep in mind that the exact steps for compiling and running the program may vary depending on the development environment or compiler you are using.
Compilation and Execution Steps:
- Write the Code:
Create a file, for example,hello.c, and paste the “Hello, World!” program into it.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello, World!\n");
return 0;
}- Open Terminal:
Open a terminal on your system. - Navigate to the File Directory:
Use thecdcommand to navigate to the directory where yourhello.cfile is located.
cd path/to/your/directory- Compile the Program:
Use thegcc(GNU Compiler Collection) command to compile the C program.
gcc hello.c -o hello- The
-oflag is used to specify the output file name. In this case, it’s namedhello.
- Run the Executable:
Execute the compiled program.
./helloYou should see the output:
Hello, World!Explanation:
- Compilation (
gcc hello.c -o hello): - The C compiler (
gcc) translates the C source code (hello.c) into machine code and creates an executable file (hello). - Execution (
./hello): - The
./hellocommand runs the compiled program (hello). The./is used to specify the current directory. - Output:
- The program’s output, “Hello, World!”, is displayed on the terminal.
Tips:
- Ensure that you have GCC installed on your system. You can install it using your system’s package manager. For example, on Debian-based systems:
sudo apt-get install gcc- The compilation and execution steps may vary slightly on different operating systems or development environments.
- Understanding these steps will help you with more complex C programs as you continue your programming journey.
Latest posts by Mahesh Wabale (see all)
- AnchorSetup using Docker-Compose - October 18, 2024
- Devops assignment - October 17, 2024
- Deployment of vault HA using MySQL - September 18, 2024

