What is EKS in AWS?
What is Amazon EKS?
Amazon EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service) is a managed service by AWS that helps you run Kubernetes without needing to set up or manage the Kubernetes control plane yourself.
With EKS:
- You can automate the deployment, scaling, and management of your containerized applications.
- It saves time and effort because AWS handles the hard parts like availability, updates, and security.
- It supports most operating systems, so you can run your applications across different platforms easily.
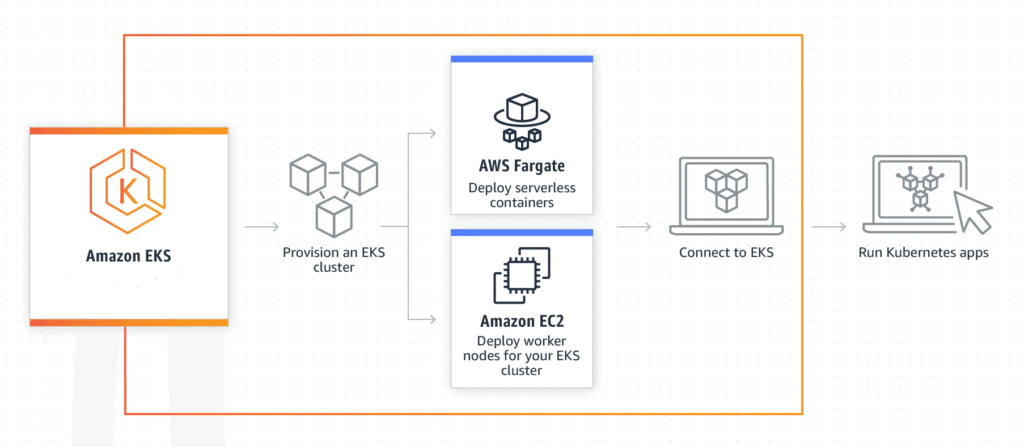
Key Features of Amazon EKS
- Secure Networking and Authentication
Amazon EKS ensures your Kubernetes applications are safe. It uses AWS’s secure network and IAM (Identity and Access Management) for login and permissions. - Easy Cluster Scaling
You can easily grow or shrink your EKS cluster depending on your needs. It supports autoscaling of both pods and nodes based on traffic and usage. - Managed Kubernetes Service
EKS manages Kubernetes for you. You can create and manage clusters using tools like:eksctl(a command-line tool)- AWS Console
- AWS CLI
- High Availability
The EKS control plane runs in multiple AWS Availability Zones, which means your cluster is protected from failures and is always available. - Integration with AWS Services
EKS connects well with other AWS services like CloudWatch, IAM, VPC, ALB, and more. This makes your container apps more powerful and easier to manage.
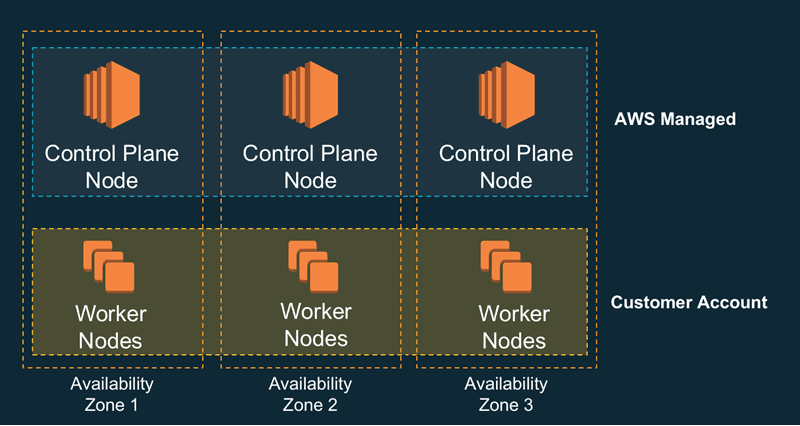
How Amazon EKS Works
- Amazon EKS runs the Kubernetes control plane (the brain of Kubernetes) across multiple data centers (Availability Zones).
- It automatically replaces any broken control plane instance.
- It also automatically upgrades and patches the control plane to keep your cluster secure and updated.
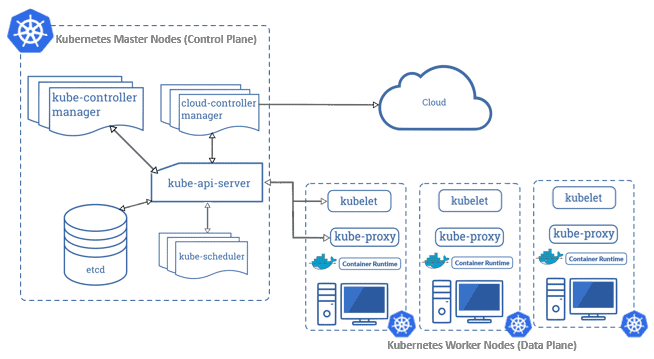
Amazon EKS Components
1) Nodes in Amazon EKS
In Amazon EKS, a Node is either a virtual or physical machine that helps run your Kubernetes workloads. There are two main types of nodes:
Master Nodes (Managed by EKS)
These nodes manage the control plane of Kubernetes — the brain of your cluster. You don’t need to create or manage them manually — EKS handles them for you.
Components of Master Node:
This is a distributed key-value store. It keeps all the important cluster configuration data and ensures it’s highly available.
API Server:
It acts as a communication hub. Whether you’re using kubectl (Kubernetes CLI) or sending a REST API call, the API Server handles it.
etcd:
This is a distributed key-value store. It keeps all the important cluster configuration data and ensures it’s highly available.
- Controller Manager:
- This part manages cloud resources (like VMs, storage, and databases).
- It keeps track of how many containers are running and ensures that everything stays in the desired state.
- Scheduler:
- It decides which work should be done and when.
- It works closely with the API server and Controller Manager to place workloads (pods) on the right nodes.
Worker Nodes
These nodes are the machines (EC2 instances or Fargate tasks) where your applications actually run.
Key components of Worker Nodes:
- kubelet:
- It communicates with the API Server to make sure the containers in each pod are running properly.
- kube-proxy:
- It manages networking and access rules.
- Think of it like a firewall and load balancer that handles communication between pods and external traffic.
2) Pods: A group of containers is called pods. They share networking, storage, IP address, and port spaces.
3) DaemonSet: It makes sure that all node runs a copy of a certain pod. It is like a monitoring tool.
Amazon EKS Workflow
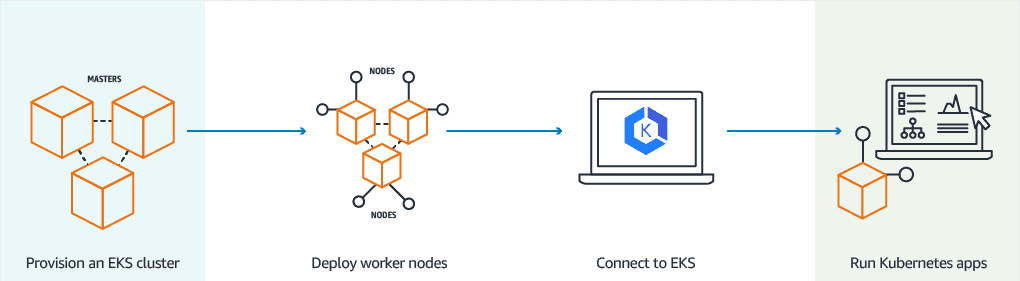
- Create an EKS Cluster
You can create a new EKS cluster using the AWS Console, AWS CLI, or any AWS SDK (like Python SDK – Boto3). - Add Worker Nodes
After creating the cluster, you need to add worker nodes (EC2 instances or Fargate).
AWS provides a ready-made template that automatically sets up and configures the nodes. - Set Up Kubernetes Tools
Now, configure tools likekubectl(Kubernetes command-line tool) to connect to your EKS cluster. - Deploy Your Application
Once everything is ready, you can deploy your application to the Kubernetes cluster.
Use Cases of Amazon EKS
- Run in Hybrid Environments
You can manage applications both on AWS and in your own data centers using the same Kubernetes tools. - Machine Learning Workflows
Train machine learning models using EC2 and tools like Kubeflow, and deploy them on EKS. - Web Applications
Easily create and run scalable, high-availability websites or applications with Kubernetes on EKS.
Benefits of Amazon EKS
Simplified Deployment: Amazon EKS automates the deployment and management of Kubernetes, reducing complexity and freeing up resources for other tasks.
Scalability and Flexibility: With Amazon EKS, your organization can easily scale containerized applications to meet changing demands, without sacrificing reliability or performance.
Security: Amazon EKS is designed to meet the strictest security standards, with features like network isolation, role-based access control, and integration with other AWS security services.
Observability: Amazon EKS integrates with AWS monitoring and logging services to provide comprehensive observability into your Kubernetes clusters.
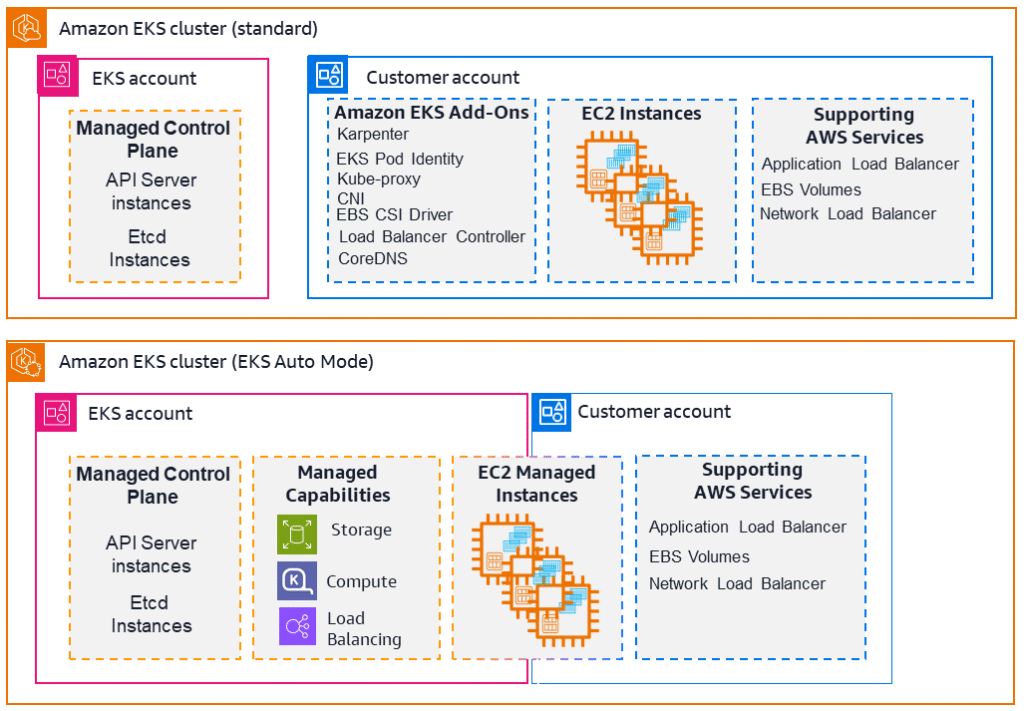
The following diagram illustrates how Amazon EKS integrates your Kubernetes clusters with the AWS cloud, depending on which method of cluster creation you choose:
Conclusion
Amazon EKS simplifies the process of deploying, managing, and scaling applications on Kubernetes, making it an ideal choice for businesses looking to leverage the power of containerized applications. For a deeper dive into the capabilities and benefits of Amazon EKS
- AI Tools for Developers: Top AI Tools Every Developer Should Know in 2026 - February 12, 2026
- What is AI? 7 Powerful and Easy Facts – Complete Beginner Guide - February 12, 2026
- How to Set Up an Okta Account – Easy & Secure Step-by-Step Guide for 2026 - January 9, 2026

